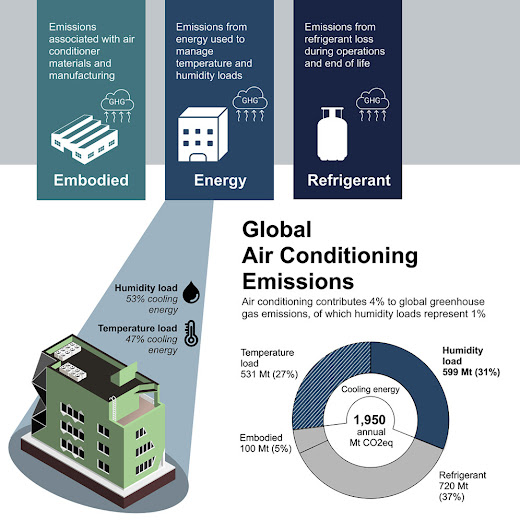
Is this the right time to buy Green?
From tomorrow (1st of April) There will be No vat on energy saving materials such as solar panel installation, heat pumps it the UK. So in this episode we answer is this the right time to invest in renewable energy for your home! But beware the small print - this new scheme only covers new systems, not so much addons to current ones! There are new types of solar panels coming to the market, that are both solar thermal and photovoltaic. These keep the panels cooler in summer and increase the efficiency. With the price of Gas going up solar thermal can really effectively cut the hot water bills in the spring, summer and autumn.